
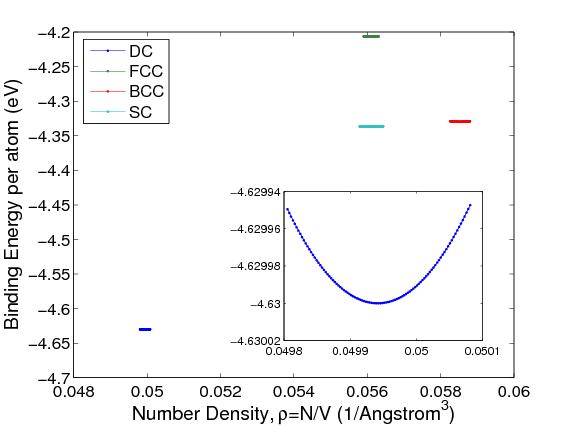
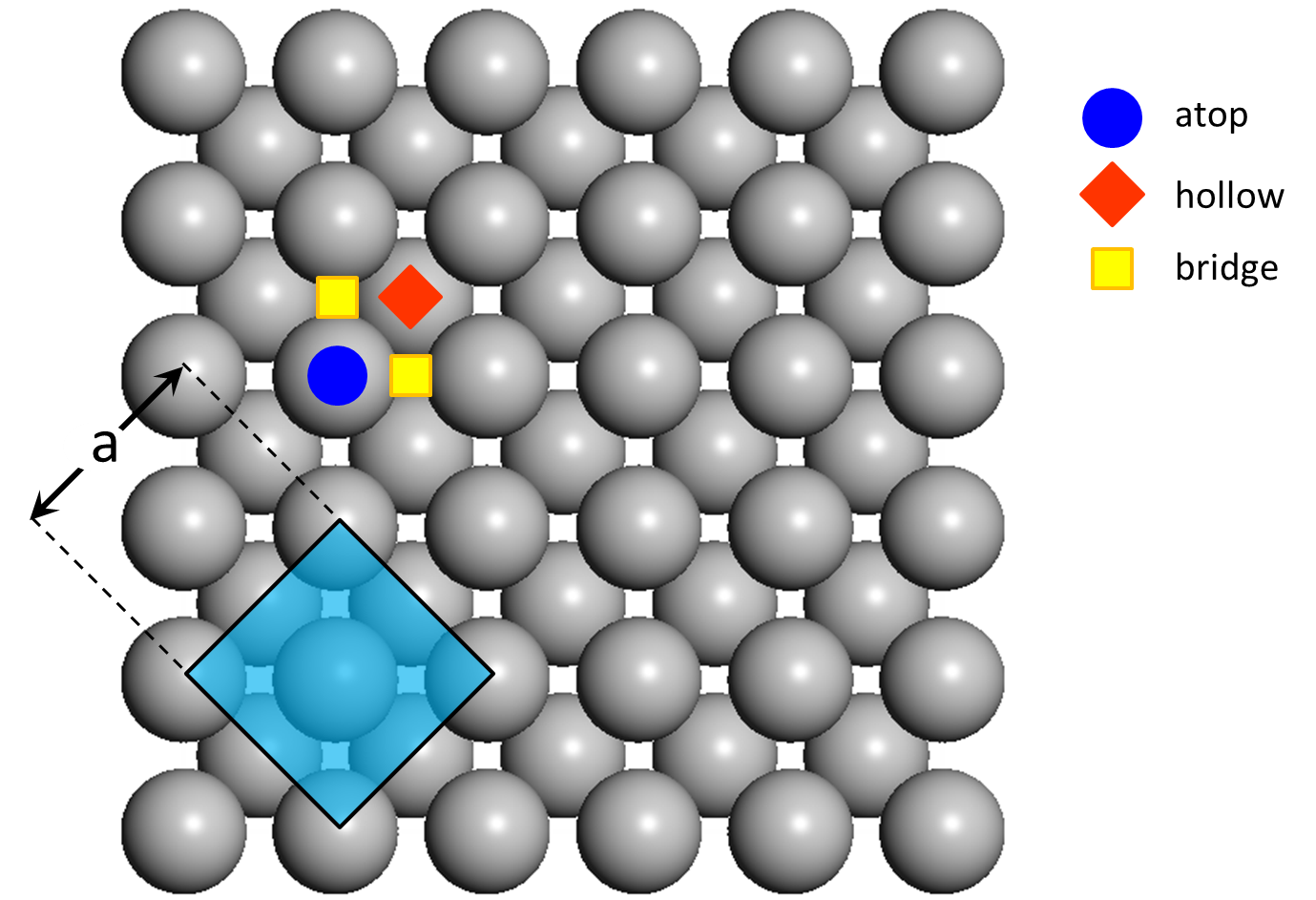
Lattice constants can be determined using techniques such as X-ray diffraction or with an atomic force microscope. Lattice constants are typically on the order of several angstroms. As lattice constants have the dimension of length, their SI unit is the meter. This deviation is especially important in nanocrystals since surface to nanocrystal core ratio is large. Near the crystals surface, lattice constant is affected by the surface reconstruction that results in a deviation from its mean value. Furthermore, in real applications, typically the average lattice constant is given. The structure is equilateral although its actual shape can not be determined from only the lattice constant.
#SI LATTICE CONSTANT FULL#
However, the full set of lattice parameters consist of the three lattice constants and the three angles between them.įor example the lattice constant for a common carbon diamond is a = 3.57Å at 300 K. A group of lattice constants could be referred to as lattice parameters. Similarly, in hexagonal crystal structures, the a and b constants are equal, and we only refer to the a and c constants. However, in the special case of cubic crystal structures, all of the constants are equal and we only refer to a. Lattices in three dimensions generally have three lattice constants, referred to as a, b, and c.

The lattice constant, or lattice parameter, refers to the constant distance between unit cells in a crystal lattice. The angles α, β, and γ are usually specified in degrees.įreebase Rate this definition: 2.0 / 1 vote Lattice Constant at 300 K (Å) C: Carbon (Diamond) Diamond: 3.56683: Ge: Germanium: Diamond: 5.64613: Si: Silicon: Diamond: 5.43095: Sn: Grey Tin: Diamond: 6. Their SI unit is the meter, and they are traditionally specified in angstroms (Å) an angstrom being 0.1 nanometer (nm), or 100 picometres (pm). When Si 1x Ge x or GaAs 1y P y layers are grown on the Si substrate, strain misfit increases with increasing Ge or Arsenide (As) fraction because the difference between Si and the grown layer lattice constants increases. The three numbers represent the size of the unit cell, that is, the distance from a given atom to an identical atom in the same position and orientation in a neighboring cell (except for very simple crystal structures, this will not necessarily be disance to the nearest neighbor). The crystal lattice parameters a, b, and c have the dimension of length. A simple cubic crystal has only one lattice constant, the distance between atoms, but in general lattices in three dimensions have six lattice constants: the lengths a, b, and c of the three cell edges meeting at a vertex, and the angles α, β, and γ between those edges. Saraswat, T.-J.Wikipedia Rate this definition: 0.0 / 0 votesĪ lattice constant or lattice parameter is one of the physical dimensions and angles that determine the geometry of the unit cells in a crystal lattice, and is proportional to the distance between atoms in the crystal. Ashburn: Silicon-Germanium Heterojunction Bipolar Transistors (Wiley, Chichester 2003)ĭ.S. Bonar: Process Development and Characterisation of Silicon and Silicon–Germanium Grown in a Novel Single-Wafer LPCVD System, PhD Thesis (University of Southampton, Southampton 1996) Madelung (Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York 1982) H. Landolt, R. Bornstein: Numerical Data and Functional Relationships in Science and Technology, Vol. Poortmans: Low Temperature Epitaxial Growth of Silicon and Strained Si 1− xGe x Layers and Their Application in Bipolar Transistors, PhD Thesis (University of Leuven, Leuven 1993)
Finally, the properties of polycrystalline silicon-germanium are discussed in the context of its use as a gate material for MOS transistors. The growth of silicon-germanium is considered, with particular emphasis on the chemical vapour deposition technique and selective epitaxy. This chapter reviews the properties of silicon-germanium, beginning with the electronic properties and then progressing to the optical properties. Strain is incorporated into the silicon-germanium or the silicon during growth, which also gives improved physical properties such as higher values of mobility.
The key benefit of silicon-germanium is its use in combination with silicon to produce a heterojunction. It also has interesting optical properties that are increasingly being applied in silicon-based photonic devices. ) and BiCMOS (bipolar CMOS) technologies. Evolution of shape, height and in-plane lattice constant of Ge- rich islands during capping with Si. The lattice constant of silicon, a Si, is 0.543 nm, the lattice constant of germanium, a Ge, is 0.566 nm and the lattice mismatch is 4.2. ) transistors for advanced complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor ( GlossaryTermCMOS Silicon-germanium is an important material that is used for the fabrication of SiGe heterojunction bipolar transistors and strained Si metal-oxide-semiconductor ( GlossaryTermMOS


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
