
It uses an abundant element, emits zero greenhouse gases, and, unlike nuclear fission, does not produce long-lived radioactive waste. Nuclear fusion is a process that releases, in the words of the International Atomic Energy Agency, “massive amounts of energy.” It’s hard to understate the promise nuclear fusion holds: It has the potential to produce nearly four million times more energy than traditional fossil fuel resources like gas, coal and oil. “The goal was to do essentially what they have just done,” he said, adding this approach is one of a few leading methods to producing nuclear fusion. This is one reason why the technology would still take years to commercialize.Īccording to David Hammer, a Cornell University professor who has been studying nuclear fusion for roughly 50 years, a successful net energy gain based on inertial confinement fusion means the lab has realized its core mission. And although it is true that huge amounts of energy can be released, considerable effort is needed to do. Given that it requires great energy separate two nucleons, it may come as a surprise to learn that splitting a nucleus can release vast potential energy.

In 2009, the lab completed construction on the National Ignition Facility, which aims to explore “clean, sustainable sources of energy.” The facility began looking into what is known as inertial confinement fusion, which uses a laser to repeatedly hit a spec of hydrogen plasma.Īt the moment, this form of fusion experiment takes up a lot of space: The National Ignition Facility is the size of three football fields. In simplest terms, nuclear fission is the splitting of an atomic bond. Here's HowĬreated by the United States government in the 1950s, the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory has been studying nuclear technology since the height of the Cold War. Tracers are used in the diagnosis of cancer and other diseases.To support our nonprofit environmental journalism, please consider disabling your ad-blocker to allow ads on Grist. Radioactive tracers are radioactive atoms that are incorporated into substances so that the movement of these substances can be tracked by a radiation detector. Fusion reactions take place in a state of matter called plasma a hot, charged gas made of positive ions and free-moving electrons with unique properties distinct from solids, liquids or gases. Nuclear Fusion is the opposite of nuclear fission reaction, in which heavy elements diffuse and form lighter elements. The nuclear fusion process occurs in elements that have a low atomic number, such as hydrogen. Radiation treatment is risky because some healthy cells are also killed, and cells at the center of a cancerous tumor can become resistant to the radiation. Nuclear fusion is the process by which two light atomic nuclei combine to form a single heavier one while releasing massive amounts of energy. Nuclear fusion is a reaction through which two or more light nuclei collide to form a heavier nucleus. Thus, the cells in the cancerous area are killed by the exposure to high-energy radiation.
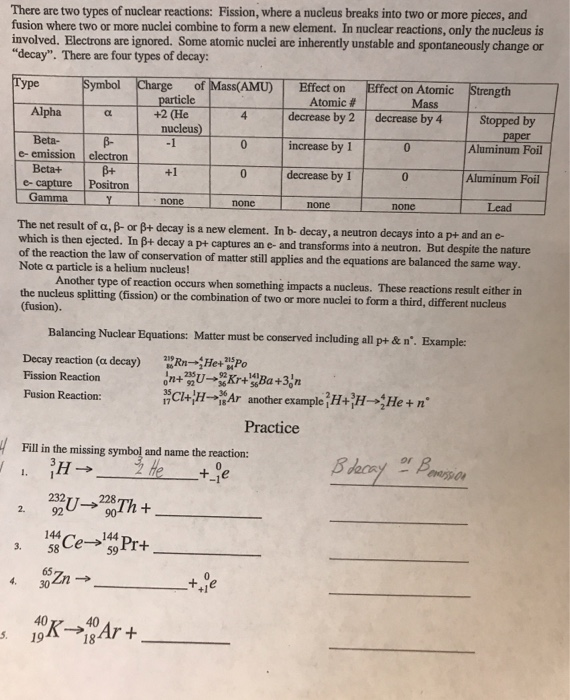
Fusion combines atomic nuclei and fission splits nuclei. The faster growing cancer cells are exposed to the radiation and are more susceptible to damage than healthy cells. In a nuclear fusion reaction, two small, light nuclei combine to form one larger, heavier nucleus. Radioactive nuclides, such as cobalt-60, are frequently used in medicine to treat certain types of cancers. Film badges are removed and analyzed at periodic intervals to ensure that the person does not become overexposed to radiation on a cumulative bases. A film badge consists of several layers of photographic film that can measure the amount of radiation to which the wearer has been exposed.
#Two nuclei combine to form one nucleus in nuclear fission. portable#
Workers who are at risk of exposure to radiation wear small portable film badges. We all know that when a heavy nucleus of uranium 235 breaks into two fragments of two different lighter nuclei of barium and krypton accompanied by 3 faster. \): A Geiger counter is used to detect radiation.Ī scintillation counter is a device that uses a phosphor-coated surface to detect radiation by the emission of bright bursts of light.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
